Leave Your Message
In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, the demand for efficient and precise joining techniques has led to the growing popularity of the Small Ultrasonic Welder. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the ultrasonic welding market is projected to reach USD 3.3 billion by 2026, driven by industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices seeking to streamline production processes while maintaining high-quality standards.

The versatility and compact size of Small Ultrasonic Welders allow them to seamlessly fit into various production environments, making them an ideal choice for companies looking to enhance their operational efficiency. This guide aims to provide an insightful overview of the critical factors to consider when selecting the best Small Ultrasonic Welder to meet your specific production needs, ensuring not only compatibility with your applications but also optimal performance and return on investment.
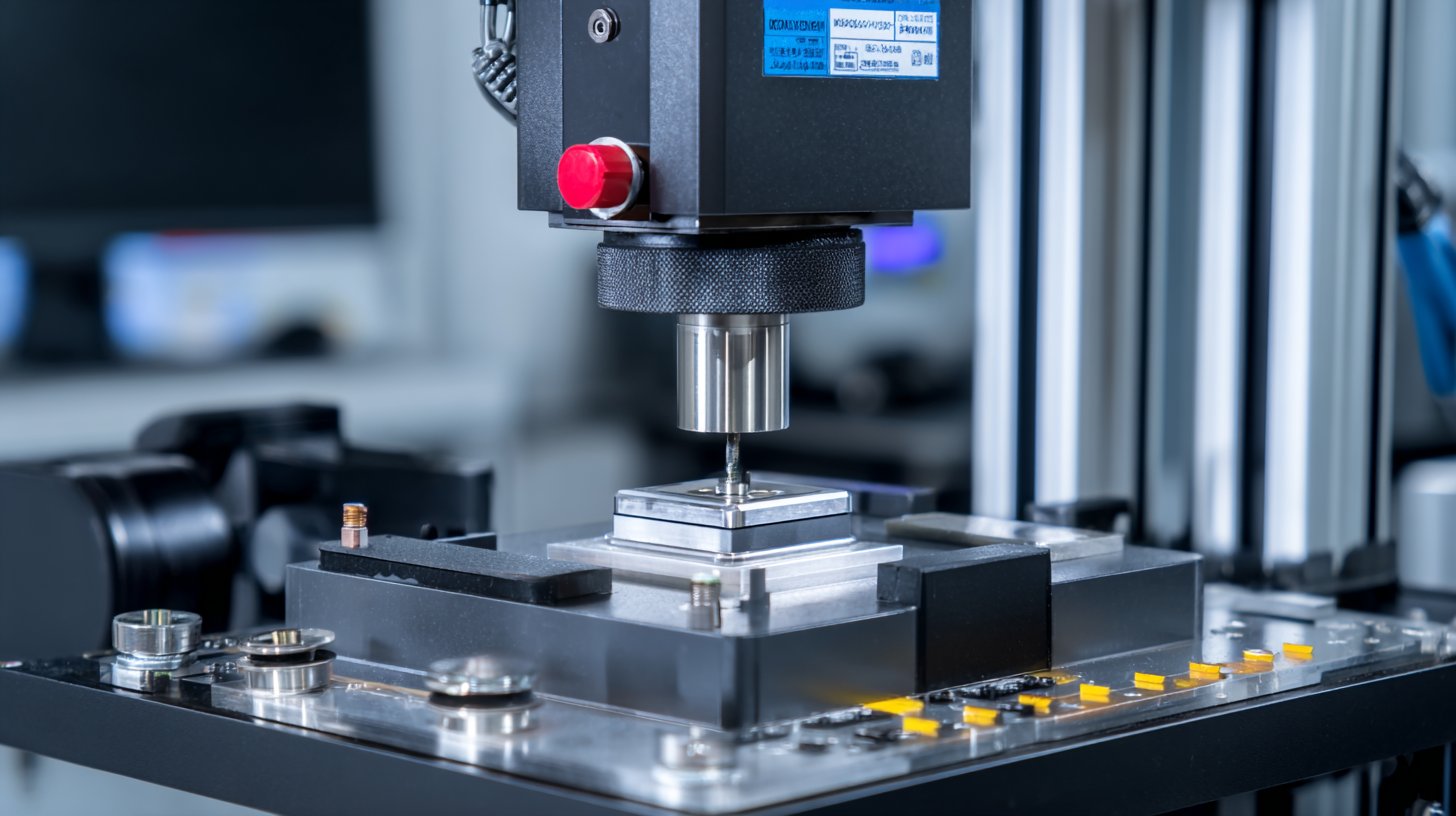
When selecting an ultrasonic welder for small parts, it's essential to consider several key factors to ensure it aligns with your production needs. First, assess the material types you will be working with. Ultrasonic welding is particularly effective for thermoplastic materials, making it a preferred choice in industries such as medical devices. Understanding the specific requirements of the materials, including their thickness and melting points, can significantly influence the welding process and the welder’s performance.
Another crucial consideration is the size of the parts being welded. Ultrasonic welding and resistance welding are the go-to methods for assembling smaller components—typically those palm-sized or smaller. Look for a machine that offers adjustable settings to accommodate varying part sizes and shapes, along with the necessary tooling to ensure precision and repeatability in your welds. Additionally, the welder's frequency and power settings play a vital role in achieving optimal welding quality, especially for intricate designs or delicate textiles commonly used in medical applications. By focusing on these factors, you can select an ultrasonic welder that enhances efficiency and reliability in your production process.
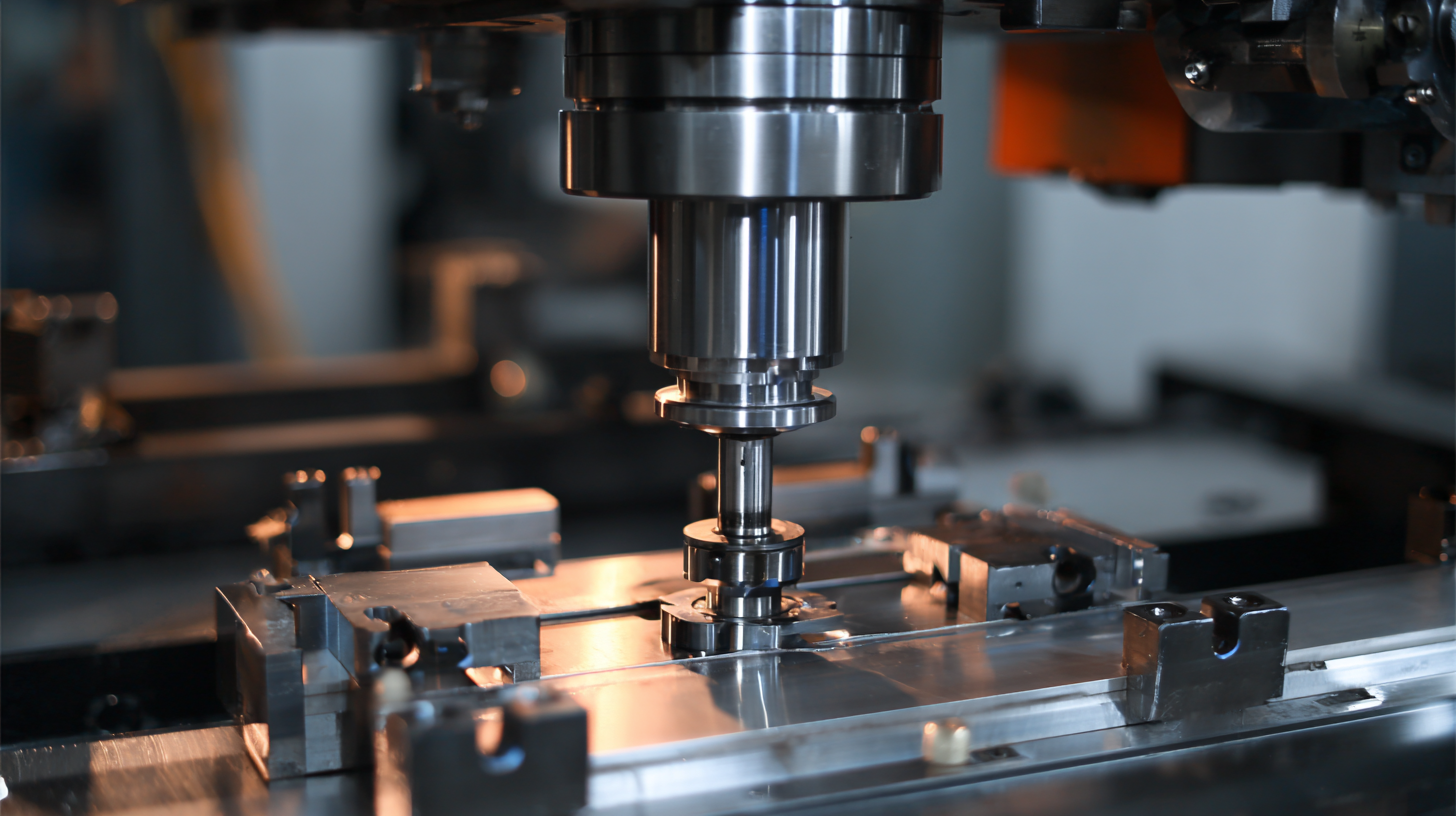

When selecting a small ultrasonic welder, understanding the significance of power output is crucial for optimizing welding performance. The power output of an ultrasonic welder, typically measured in watts, directly affects the efficiency and quality of the welding process. According to industry reports, welders with power outputs ranging from 100 to 1000 watts are commonly used in small-scale applications, highlighting the diverse needs of production environments. High-frequency vibrations produced at these power levels ensure effective bonding of materials, which is particularly vital in industries such as medical devices, automotive, and consumer electronics.
An optimal power range ensures that the welder can adapt to different materials and thicknesses, providing flexibility for manufacturers. Research has shown that a well-calibrated ultrasonic welder can achieve bond strengths exceeding 90% of the parent material, underscoring the importance of selecting a machine that delivers adequate power for specific applications. Investing in a small ultrasonic welder with adjustable power settings allows operators to fine-tune the process based on material characteristics, minimizing defects and reducing waste. As the demand for precision in manufacturing increases, the role of power output remains a pivotal consideration for achieving superior results in ultrasonic welding.
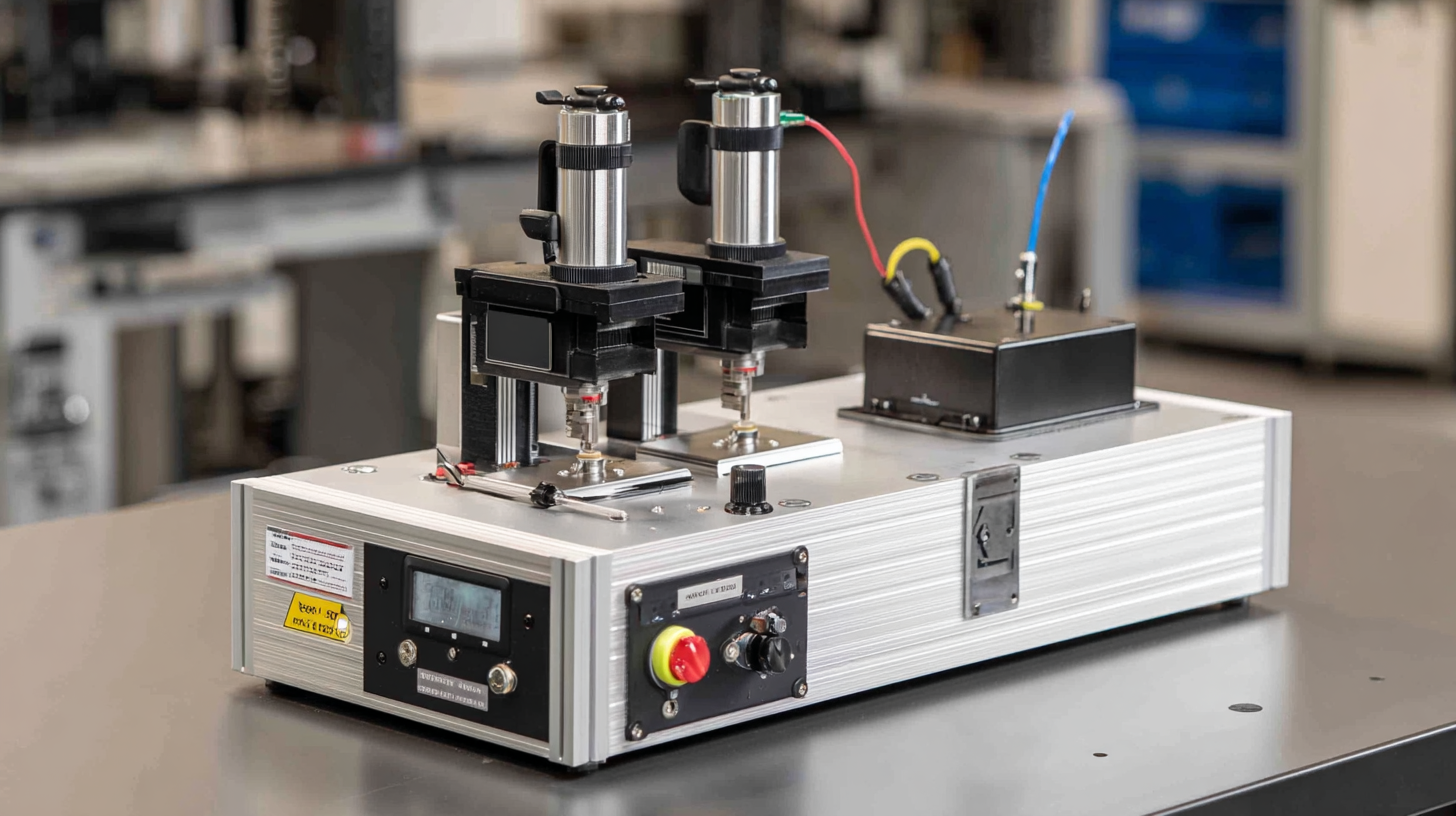
When selecting a small ultrasonic welder, evaluating its size and weight is crucial, especially when working within limited production spaces. A compact welder not only saves valuable floor space but also enhances mobility, allowing operators to easily reposition the machine as production needs shift. It's essential to measure the available workspace and consider the layout of the production area to ensure that the welder can be integrated seamlessly without hindering workflow.
Additionally, the weight of the ultrasonic welder can impact its stability and portability. Lightweight models are easier to move and adjust, which can be beneficial for small-scale or multi-tasking environments. However, it's important to balance portability with stability; a welder that is too light may not provide the necessary stability during operation, potentially affecting the quality of the welds. Therefore, prospective buyers should carefully consider the specific demands of their production environment, ensuring that the chosen welder optimally fits both the physical space and operational requirements.
When selecting the best small ultrasonic welder for your production needs, understanding the various ultrasonic welding technologies available on the market is critical. Ultrasonic welding is increasingly favored for its efficiency and effectiveness in joining materials, especially in industries such as automotive and packaging. For example, nonwoven fabrics are transformed into essential personal protective equipment using ultrasonic welding equipment, showcasing how this technology is integral to modern manufacturing processes.
Different ultrasonic welding methods can significantly impact product quality and production speed. Technologies vary in terms of frequency, power output, and the materials they can effectively bond. Each option presents unique advantages; therefore, evaluating factors such as the type of materials to be welded, the scale of production, and the desired joint strength is essential. As industries continue to innovate, keeping abreast of technological advancements will help manufacturers make informed decisions on the optimal ultrasonic welding technology for their specific requirements.
When selecting a small ultrasonic welder, balancing cost and efficiency is crucial, especially as the demand for greater flexibility and customization grows in industries like hygiene manufacturing. Companies are often faced with a choice between cheaper options that may compromise performance and higher-end models that provide superior efficiency but come at a premium price.
To achieve the right balance, consider the specific needs of your production process. Assess not only the initial cost of the welder but also its operational efficiency, reliability, and the technical support available. Investing in a more efficient model might reduce long-term costs through lower energy consumption and less downtime, proving beneficial in the long run.
Tips: First, evaluate the materials and components you intend to weld—this will guide you in determining the necessary power levels and specifications for your welder. Second, don’t forget to factor in the machine’s versatility. A welder that can easily adapt to various applications may save you from purchasing additional equipment later. Finally, review user feedback and performance data; real-world experiences often provide insights that specifications alone cannot.